- Published on
How to handle concurrent access and modify in database using Isolation (ACID properties)
- Authors

- Name
- Minh LK
00. Tóm tắt
- Isolation Level dùng để defined cách các transactions “đọc” kết quả của nhau.
- Locking mechanisms (PL, OL) dùng để control cách “đọc, ghi” data giữa các sessions trên cùng 1 dòng.
- Cả hai cơ chế đều dùng cho concurrent transactions (Data Race)
- Isolation Level càng cao thì consistent càng cao và concurrent càng thấp
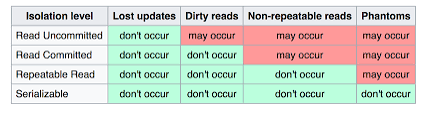
I. Transaction Isolation Level
**Primary for InnoDB, MyISAM don’t support full ACID
1. Read uncommitted
- Allow to read data from uncommitted transaction (session)
2. Read Committed
- Allow to read data from committed transaction during the transaction
3. Repeatable Read
- Read the same row data during the transaction
- Phantom may occur
- RR help to avoid seeing change from existing row data, NOT when data is inserted new
- Phantom read means read data that is inserted new
4. Serializable (Tuần tự)
- All transaction are performed one by one serializable.
II. Locking Mechanism - Pessimistic Locking and Optimistic Locking
- A technique to control multi-transaction/multi-session read/write same data
1. Pessimistic Locking (Default for morden DBMS)
- Usually for DBMS level
- Write operation one by one
- Locks row, table until the write completed
- Flow: Create lock -> update data -> release lock
- May cause deadlock.
- Recommended for
- Strong consistency - Low concurrency
- Good with high rate transaction conflict
- Reduce retry attempts.
2. Optimistic Locking
- Usually for Application level
- Allow parallel write operations
- Utilizes update timestamp / row column version
- Conflict version trigger retry or rollback
- Recommended for
- Low consistency - Strong concurrency
- Good with low rate transaction conflict
Pessimistic Lock Advanced
- Type of locks
- Shared lock (Read lock): Allow reads but not writes by other transactions
- Exclusive lock (Read-Write lock): Prevent both reads and writes
- Apply lock only when a existed lock is released.
How to enable Pessimistic Lock/ Optimistic Lock
- Pessimistic Lock
- Enable by default with the REPEATABLE_READ|SERIALIZABLE isolation level
- Optimistic Lock
- Enable by application logic.
Source
ChatGPT: The relationship is as follows:
- Optimistic Locking is often associated with lower isolation levels (e.g., "READ COMMITTED") that allow more concurrency. It assumes conflicts are rare and handles them when they occur.
- Pessimistic Locking is often associated with higher isolation levels (e.g., "REPEATABLE READ" or "SERIALIZABLE") that provide strong consistency by using locks to prevent concurrent access to data. In simple terms, isolation levels determine how much you can see of other transactions' work, while locking mechanisms (optimistic or pessimistic) control how data is accessed and modified. You choose the combination of isolation levels and locking mechanisms that best suits your application's requirements for data consistency and concurrency.
https://viblo.asia/p/010-exclusive-lock-va-shared-lock-924lJjn0lPM